By Andualem Sisay Gessesse- The relationship between Ethiopians and Kenyans is characterized by a long history of cultural, economic, and political interactions. These two neighboring countries in East Africa share many similarities, but also have distinct differences that have shaped their relationship over time.
Ethiopia and Kenya have a shared history that dates back centuries. The region has been a crossroads for trade and migration, leading to the exchange of ideas, goods, and people between the two countries. The ancient Ethiopian kingdom of Aksum had significant influence over parts of present-day Kenya, particularly in the northern regions. This historical connection has contributed to the cultural ties between the two nations.
Cultural Connections
Ethiopians and Kenyans share several cultural connections due to their proximity and historical interactions. Both countries have diverse ethnic groups with their own unique traditions, languages, and customs. However, there are also cultural similarities that can be observed. For instance, both Ethiopians and Kenyans have a strong tradition of oral storytelling, music, dance, and art. Additionally, they share a love for coffee, which is an integral part of their respective cultures.
Economic Relations
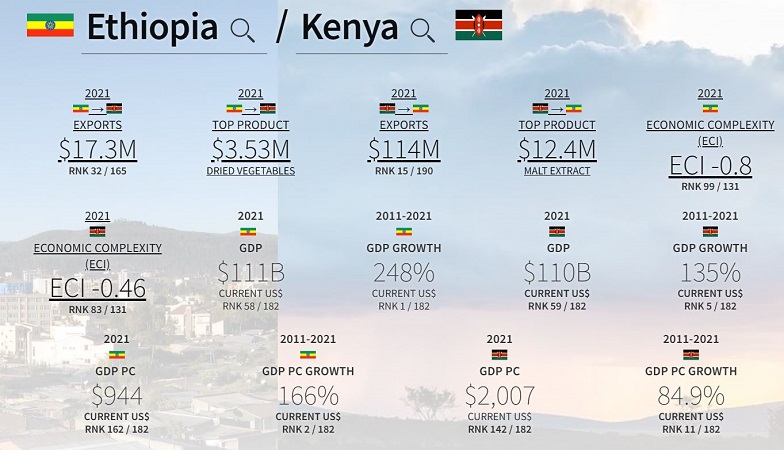
Economically, Ethiopia and Kenya have developed strong ties over the years. Trade between the two countries has been growing steadily, with both nations benefiting from the exchange of goods and services. The projected GDP (Gross Domestic Product) of Kenya for the year 2022 is $109.7 billion, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). While Ethiopia’s GDP is estimated reaching around $109.1 billion in 2022.
Ethiopia is known for its agricultural products such as coffee, tea, spices, and flowers, which are exported to Kenya. On the other hand, Kenya exports manufactured goods like textiles, machinery, and processed foods to Ethiopia. Furthermore, both countries are members of regional economic blocs such as the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) and the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), which promote economic cooperation in the region.
Political Relations
Politically, Ethiopia and Kenya have maintained diplomatic relations since their independence from colonial rule. Both countries are members of the African Union (AU) and the United Nations (UN), which provide platforms for cooperation and dialogue on regional and global issues. Over the years, they have collaborated on various initiatives, including peacekeeping missions, conflict resolution efforts, and infrastructure development projects. However, like any neighboring countries, there have been occasional tensions and disputes over border issues and resource allocation. Nevertheless, these challenges have generally been managed through diplomatic channels.
People-to-People Interactions
The relationship between Ethiopians and Kenyans is not limited to official interactions but also extends to people-to-people connections. There is a significant population of Ethiopians living in Kenya, particularly in urban centers like Nairobi. These individuals contribute to various sectors of Kenyan society, including business, education, healthcare, and the arts. Similarly, Kenyans can be found in Ethiopia, working in diverse fields such as education, tourism, and development projects. These interactions foster cultural exchange and understanding between the two nations.
In general, the relationship between Ethiopians and Kenyans is multifaceted and encompasses historical, cultural, economic, political, and people-to-people dimensions. While they share a common border and have a long history of interaction, each country has its own unique identity and characteristics. Nonetheless, the similarities and shared interests have contributed to a generally positive relationship between the two nations.
Political Front
Ethiopia and Kenya have a long history of political relations that can be traced back to ancient times. The two countries share a border and have been engaged in various political, economic, and social interactions over the years. This comprehensive detail will explore the historical background, key events, and current state of political relations between Ethiopia and Kenya.
The relationship between Ethiopia and Kenya dates back centuries, with both countries being part of the ancient trade routes that connected the African continent. The interactions between the people of Ethiopia and Kenya were primarily driven by trade, cultural exchanges, and occasional conflicts.
During the colonial era, both Ethiopia and Kenya were under European rule. Ethiopia managed to maintain its independence throughout this period, while Kenya was colonized by the British. Despite being under different colonial powers, Ethiopia played a significant role in supporting Kenya’s struggle for independence. Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie provided moral and financial support to Kenyan nationalists fighting against British colonial rule.
Key Events:
1. Independence Movements: In the mid-20th century, both Ethiopia and Kenya gained their independence from colonial rule. Ethiopia became independent in 1941 after successfully resisting Italian occupation during World War II. Kenya achieved independence in 1963 after a protracted struggle led by nationalist leaders such as Jomo Kenyatta.
2. Regional Cooperation: Following their independence, Ethiopia and Kenya recognized the importance of regional cooperation and joined various regional organizations such as the Organization of African Unity (OAU), now known as the African Union (AU). Both countries actively participated in promoting Pan-Africanism and advocating for African unity.
3. Border Disputes: Despite generally cordial relations, Ethiopia and Kenya have had occasional border disputes over the years. One notable dispute occurred in 2015 when tensions arose over a contested border region known as the Ilemi Triangle. However, both countries have managed to resolve these disputes through diplomatic negotiations and peaceful means.
Current State of Relations
Ethiopia and Kenya maintain diplomatic relations and engage in various bilateral activities. The two countries have signed numerous agreements covering areas such as trade, security, infrastructure development, and cultural exchanges. They also collaborate on regional issues, particularly within the framework of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), a regional organization that promotes cooperation among East African countries.
Economically, Ethiopia and Kenya have significant trade ties. Kenya serves as a major transit route for Ethiopian goods destined for international markets through the Port of Mombasa. Additionally, both countries have implemented joint infrastructure projects such as the Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia Transport (LAPSSET) corridor, which aims to enhance connectivity and boost trade in the region.
Politically, Ethiopia and Kenya have supported each other on various international platforms. They often align their positions on regional and global issues, particularly within the African Union and the United Nations. Both countries have also collaborated in peacekeeping efforts, contributing troops to various United Nations missions in conflict-affected regions.
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on enhancing people-to-people relations between Ethiopia and Kenya. This includes promoting tourism, cultural exchanges, and educational collaborations. The governments of both countries have implemented initiatives to facilitate easier movement of people across their borders, such as the introduction of electronic visas.
Economic Relations
Ethiopia and Kenya have a long history of economic relations, with both countries being important trade partners in the East African region. The economic ties between Ethiopia and Kenya encompass various sectors such as trade, investment, infrastructure development, and regional integration initiatives. This comprehensive detail will explore the different aspects of Ethiopia and Kenya’s economic relations.
Trade Relations
Ethiopia and Kenya have a significant bilateral trade relationship. Trade between the two countries has been growing steadily over the years, with both countries benefiting from the exchange of goods and services. The main commodities traded between Ethiopia and Kenya include agricultural products, textiles, machinery, chemicals, and manufactured goods.
One of the key factors driving trade between Ethiopia and Kenya is their geographical proximity. The two countries share a common border, which facilitates easy movement of goods and people. Additionally, both countries are members of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) and the East African Community (EAC), regional economic communities that promote trade integration among member states.
Investment Relations
Ethiopia and Kenya also have significant investment relations. Both countries have attracted foreign direct investment (FDI) in various sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, energy, infrastructure, and services. Kenyan companies have invested in Ethiopia’s manufacturing sector, particularly in areas such as textiles, food processing, and construction materials.
On the other hand, Ethiopian companies have also made investments in Kenya’s economy. Ethiopian Airlines, for example, has established a strong presence in Kenya’s aviation sector by operating numerous flights to different destinations within Kenya. Ethiopian banks have also expanded their operations into Kenya’s financial sector.
Infrastructure Development
Ethiopia and Kenya have collaborated on several infrastructure development projects aimed at enhancing connectivity between the two countries. One notable project is the Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia Transport (LAPSSET) Corridor. This mega-infrastructure project aims to connect Kenya’s Lamu Port to South Sudan and Ethiopia through a network of roads, railways, and pipelines. The LAPSSET Corridor is expected to boost trade and investment between Ethiopia and Kenya by providing efficient transport links.
Another significant infrastructure project is the Ethiopia-Kenya Power Interconnection Project. This project involves the construction of a high-voltage transmission line that will enable the exchange of electricity between the two countries. The power interconnection is expected to enhance energy security, promote renewable energy development, and support industrial growth in both countries.
Regional Integration Initiatives
Ethiopia and Kenya are actively involved in regional integration initiatives that aim to promote economic cooperation and integration among East African countries. Both countries are members of the EAC, which seeks to create a common market, facilitate free movement of goods and services, and promote regional economic development.
Ethiopia is also a key player in the Horn of Africa region and has been involved in various regional integration initiatives such as the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) and the African Union (AU). These regional bodies provide platforms for Ethiopia and Kenya to collaborate on issues related to trade, infrastructure development, peace, and security.
Generally, Ethiopia and Kenya have strong economic relations characterized by trade, investment, infrastructure development, and regional integration initiatives. The geographical proximity between the two countries, membership in regional economic communities, and shared development goals contribute to the deepening of their economic ties.
Trade Volume and Major Commodities
The bilateral trade volume between these two countries has been steadily increasing over the years, driven by various factors such as geographical proximity, economic complementarity, and regional integration efforts.
Major Commodities Traded:
Several major commodities are traded between Ethiopia and Kenya, contributing to the overall bilateral trade volume. These commodities include:
1. Agricultural Products: Agriculture plays a crucial role in both Ethiopia and Kenya’s economies, and as such, agricultural products form a significant portion of the bilateral trade. Key agricultural commodities traded between the two countries include coffee, tea, horticultural products (such as flowers and vegetables), cereals (such as maize and wheat), pulses (such as beans and lentils), and livestock products.
2. Manufactured Goods: Ethiopia has been experiencing rapid industrialization in recent years, leading to an increase in the export of manufactured goods to Kenya. These goods include textiles, garments, leather products, processed foods, chemicals, and construction materials. On the other hand, Kenya exports various manufactured goods to Ethiopia, including pharmaceuticals, machinery and equipment, processed foods, plastics, and electrical appliances.
3. Energy Products: Energy products also contribute to the bilateral trade between Ethiopia and Kenya. Ethiopia is known for its vast hydropower potential and exports electricity to Kenya through cross-border power transmission lines. This energy cooperation helps meet Kenya’s growing energy demands and strengthens the economic ties between the two countries.
4. Services: In addition to goods, services also play a significant role in the bilateral trade between Ethiopia and Kenya. These services include tourism, transportation, financial services, telecommunications, and professional services. Both countries have been working towards enhancing cooperation in the service sector to further boost trade and investment.
Ethiopia’s Export Kenya
Ethiopia’s export items to Kenya and export earnings have been significant in fostering economic relations between the two countries. Ethiopia, being one of the largest economies in Africa, has a diverse range of export items that cater to various sectors in Kenya’s economy. These export items contribute to Ethiopia’s export earnings and play a crucial role in strengthening bilateral trade between the two nations.
Ethiopia’s export items to Kenya encompass a wide array of products, including agricultural commodities, manufactured goods, and services. Some of the key export items from Ethiopia to Kenya include:
1. Coffee: Ethiopia is renowned for its high-quality coffee production. Coffee is one of the major export items from Ethiopia to Kenya. Kenyan consumers appreciate Ethiopian coffee for its unique flavors and aromas. The coffee trade between the two countries not only contributes to Ethiopia’s export earnings but also satisfies Kenya’s demand for premium coffee.
2. Oilseeds: Ethiopia is a significant producer of oilseeds such as sesame seeds and niger seeds. These oilseeds are exported to Kenya, where they are used in various industries, including food processing and oil extraction. The export of oilseeds from Ethiopia to Kenya helps meet the demand for these commodities in the Kenyan market.
3. Textiles and garments: Ethiopia has been making strides in developing its textile and garment industry. The country exports textiles and garments to Kenya, catering to the growing demand for affordable clothing in the Kenyan market. This trade benefits both countries by promoting industrial growth and creating employment opportunities.
4. Livestock: Livestock products, including live animals, meat, and dairy products, are also exported from Ethiopia to Kenya. These products contribute significantly to Ethiopia’s export earnings while meeting Kenya’s demand for livestock-based commodities.
5. Construction materials: Ethiopia exports construction materials such as cement, steel bars, and ceramics to Kenya. These materials are essential for Kenya’s booming construction industry, supporting infrastructure development and urbanization.
6. Fruits and vegetables: Ethiopia exports a variety of fruits and vegetables to Kenya, including avocados, mangoes, bananas, and tomatoes. These fresh produce items are in high demand in the Kenyan market and contribute to Ethiopia’s export earnings.
7. Chemicals and pharmaceuticals: Ethiopia exports chemicals and pharmaceutical products to Kenya. These items cater to Kenya’s industrial and healthcare sectors, supporting various manufacturing processes and medical needs.
8. Electronics and electrical equipment: Ethiopia also exports electronics and electrical equipment to Kenya. These products include household appliances, telecommunications equipment, and electrical components. The export of these items contributes to Ethiopia’s export earnings while meeting Kenya’s demand for consumer electronics.
Ethiopia’s export earnings from Kenya have been significant in recent years. The exact figures may vary annually due to fluctuations in trade volumes and commodity prices. However, the overall trend indicates a positive growth trajectory. In 2019, Ethiopia’s total exports to Kenya were valued at approximately $168 million USD.
It is important to note that the aforementioned export items are not exhaustive, as Ethiopia engages in trade across various sectors with Kenya. The export earnings from these items contribute to Ethiopia’s overall balance of trade and economic growth.
Kenya’s Major Export Commodities to Ethiopia
In 2019, Kenya’s total exports to Ethiopia were valued at approximately $98 million. The main export products from Kenya to Ethiopia included petroleum oils, tea, coffee, pharmaceutical products, iron and steel products, plastics, and electrical machinery. These products accounted for a significant portion of Kenya’s export earnings from Ethiopia.
However, in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on global trade, including trade between Kenya and Ethiopia. Lockdown measures, disruptions in supply chains, reduced demand, and travel restrictions affected trade flows between the two countries. As a result, Kenya’s export earnings from Ethiopia may have been affected.
According to available data, some of the key export commodities from Kenya to Ethiopia include:
1. Tea: Kenya is one of the largest tea producers in the world, and tea exports form a significant part of its economy. Ethiopia is a major importer of Kenyan tea, with a growing demand for both black and green tea varieties. The value of tea exports from Kenya to Ethiopia in US dollars fluctuates annually based on factors such as production levels, global demand, and market conditions.
2. Petroleum Products: Kenya also exports petroleum products to Ethiopia, including gasoline, diesel, and other refined petroleum products. These exports contribute to meeting Ethiopia’s energy needs and are an important component of bilateral trade between the two countries.
3. Cement: Kenya is known for its cement production capacity, and Ethiopian construction industry heavily relies on imported cement. Kenyan cement manufacturers export significant quantities of cement to Ethiopia, contributing to the development of infrastructure projects in the country.
4. Pharmaceuticals: Kenya has a well-established pharmaceutical industry that exports various medicines and healthcare products to Ethiopia. This includes both generic drugs and branded pharmaceuticals.
5. Building Materials: Other building materials such as iron sheets, steel bars, and construction equipment are also exported from Kenya to Ethiopia. These materials are essential for the construction sector in Ethiopia, which is experiencing rapid growth.
6. Agricultural Products: Kenya exports a range of agricultural products to Ethiopia, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and livestock products. These exports help meet Ethiopia’s food requirements and contribute to food security in the country.
7. Textiles and Apparel: The textile and apparel industry in Kenya exports garments and fabrics to Ethiopia. This sector has seen significant growth in recent years due to favorable trade agreements and increasing demand for Kenyan textiles in the Ethiopian market.
8. Electrical Equipment: Kenya exports electrical equipment, including generators, transformers, and other electrical components, to Ethiopia. These products are crucial for Ethiopia’s expanding energy infrastructure and industrial development.
It is important to note that the value of these export commodities can vary from year to year due to factors such as changes in demand, global market conditions, and economic fluctuations. The figures provided here are based on available data but may not represent the most current values.
People to People Relations
Ethiopia and Kenya share a long history of social relations, characterized by cultural, economic, and political interactions between the people of both countries. These relations have evolved over time and have been shaped by various factors such as geographical proximity, historical ties, and shared cultural heritage.
Historic
The social relations between Ethiopia and Kenya can be traced back to ancient times when trade routes connected the two regions. The Axumite Empire, which was centered in present-day Ethiopia, had extensive trade networks that reached as far as the Kenyan coast. This facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices between the two regions.
Cultural Interactions
Ethiopia and Kenya are home to diverse ethnic groups with rich cultural traditions. The Oromo, Amhara, and Tigray people in Ethiopia have historical connections with various ethnic groups in Kenya such as the Borana, Gabra, and Rendille. These connections are evident in shared cultural practices, including music, dance, folklore, and traditional ceremonies.
Economic Relations
Economic ties between Ethiopia and Kenya have grown significantly in recent years. Both countries are members of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), which promote regional integration and trade cooperation. The construction of infrastructure projects such as roads and railways has further enhanced economic connectivity between the two nations.
Political Cooperation
Ethiopia and Kenya have maintained diplomatic relations since their independence from colonial rule. Both countries are active members of regional organizations such as the African Union (AU) and the United Nations (UN). They have collaborated on various political issues, including peacekeeping efforts in conflict-affected regions such as Somalia and South Sudan.
Tourism and People-to-People Exchanges
Tourism plays a significant role in fostering social relations between Ethiopia and Kenya. Many tourists from Ethiopia visit Kenya to explore its diverse wildlife, national parks, and historical sites such as the Maasai Mara and Lamu Island. Similarly, Kenyan tourists visit Ethiopia to experience its rich cultural heritage, ancient historical sites like Lalibela, and natural wonders like the Simien Mountains.
People-to-people exchanges between Ethiopia and Kenya have also been facilitated through educational programs, cultural festivals, and sports events. Students from both countries often pursue higher education in each other’s universities, contributing to cross-cultural understanding and knowledge exchange.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the social relations between Ethiopia and Kenya are generally positive, there have been occasional challenges. Border disputes, particularly along the shared border in the Omo River region, have strained relations at times. However, both countries have shown a commitment to resolving these issues through diplomatic channels.
Opportunities
The ongoing development of regional infrastructure projects such as the Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia Transport (LAPSSET) corridor presents opportunities for further enhancing social relations between Ethiopia and Kenya. This project aims to improve connectivity and trade links between the two countries, fostering economic integration and people-to-people interactions.
In conclusion, Ethiopia and Kenya share deep-rooted social relations that are shaped by historical, cultural, economic, and political factors. These relations continue to evolve and contribute to mutual understanding, cooperation, and regional integration.