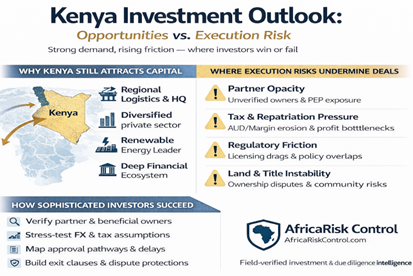
Mekele, the Capital of Tigray Region of Ethiopia provides land for investors who are set to create jobs for 22,900 youth.
The 222 investors who secured the land have registered a total capital of 13.6 billion birr (about $483 million). The investors who secured land from Mekele City Administration on Saturday will be engaged in manufacturing and service sectors, according to Fana Broadcasting.
As the demand to invest in the region has been increasing Mekele City Administration has been providing land after evaluating investment proposals of the investors.
The report indicated that Dr. Debretision Gebremichael, Deputy Head of Tigray Region said that when more investment comes to the region, more youth will get jobs.
In recent years youth unemployment in Ethiopia has been a major concern. For some cities the unemployment rate is estimated to reach up to 30% though the official data says that the national unemployment rate is around 24%.
The growing rural to urban migration and the imbalance between the number of graduates coming from schools every year and the number of jobs the country is providing, have increased the unemployment rate in cities including Mekele.
The December 2016 report of the World Bank on employment in Ethiopia suggested that the government needs to address major obstacles in the labor market to enable the country accelerate structural transformation, ensure inclusive growth and lead to poverty reduction.
Entitled, ‘5th Ethiopia economic update: why so idle? – wages and employment in a crowded labor market, World Bank’s report offers five policy recommendations to enhance urban labor markets:
– encourage firm creation and firm growth that creates jobs for non-graduates;
– increase labor productivity in the low-skill population segment by addressing constraints faced by firms in accessing capital (financial and physical) to ensure that the marginal product of labor increases above the nutrition-based wage;
– invest further in job training and technical training programs to build the skills of those in the job market: both for low-skilled workers to increase their productivity and for those with higher levels of education to increase their skill base;
– introduce targeted urban safety nets and labor market programs to invest in skills of low skilled employees and the unemployed, and provide financial support to enable their job search;
– enhance the use of information communication and technology (ICT) to provide information on job vacancies throughout the city and reduce the cost of job search.