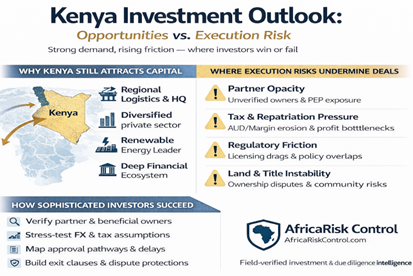
By Woubishet Sisay – Ethiopia, located in the Horn of Africa, has been making significant strides in developing its infrastructure over the past few decades.
The country has recognized the importance of robust infrastructure in driving economic growth, improving living standards, and attracting foreign investment. In this comprehensive response, we will explore various aspects of Ethiopia’s infrastructure, including transportation, energy, telecommunications, water supply, and housing.
Transportation Infrastructure
Ethiopia has been investing heavily in its transportation infrastructure to enhance connectivity within the country and with neighboring countries. The road network is a crucial component of Ethiopia’s transportation system. The Ethiopian Roads Authority (ERA) is responsible for planning, constructing, and maintaining the road network. The major highways in Ethiopia include the Addis Ababa-Adama Expressway, Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway Corridor, and the Trans-African Highway Network.
The railway system is another vital part of Ethiopia’s transportation infrastructure. The Ethiopian Railway Corporation (ERC) has been working on expanding the railway network to improve freight and passenger transport. Notable projects include the Addis Ababa Light Rail Transit (LRT) system, which began operations in 2015, and the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway line connecting Ethiopia with Djibouti’s port.
Air transportation is facilitated by the Ethiopian Airlines Group, which operates one of Africa’s largest and most successful airlines. Ethiopian Airlines connects Ethiopia to various international destinations and plays a crucial role in promoting tourism and trade.
Energy Infrastructure
Ethiopia has been focusing on developing its energy infrastructure to meet growing domestic demand and become a regional exporter of electricity. The country has abundant renewable energy resources, particularly hydroelectric power potential. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), currently under construction on the Blue Nile River, is set to become Africa’s largest hydropower project upon completion.
In addition to hydropower, Ethiopia is also exploring other renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. The country has several wind farms, including the Ashegoda Wind Farm, which is one of the largest in Africa. The government has also implemented various initiatives to promote solar energy, including the Solar Home Systems program.
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Ethiopia has made significant progress in expanding its telecommunications infrastructure, particularly in mobile and internet connectivity. The state-owned Ethio Telecom is the major telecommunications service provider in the country. Efforts have been made to improve network coverage and increase internet penetration rates.
The government has also initiated the Ethio-Djibouti Regional Interconnection Project, which aims to connect Ethiopia with submarine fiber optic cables, enhancing international connectivity and reducing reliance on satellite communication.
Water Supply and Sanitation Infrastructure
Access to clean water and sanitation facilities is a critical aspect of infrastructure development. In Ethiopia, the Ministry of Water, Irrigation, and Energy is responsible for water supply and sanitation services. The government has been working on improving access to safe drinking water sources and sanitation facilities, particularly in rural areas.
Various projects have been implemented to increase water supply coverage, such as the construction of dams, reservoirs, and water treatment plants. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) have provided a framework for Ethiopia’s efforts to achieve universal access to clean water and sanitation.
Housing Infrastructure
Ethiopia has been experiencing rapid urbanization, leading to increased demand for housing. The government has implemented various programs to address this need, including the Integrated Housing Development Program (IHDP). The IHDP aims to provide affordable housing options for low-income individuals and families through partnerships between the government and private developers.
In addition to affordable housing initiatives, Ethiopia has also seen significant investment in high-end real estate developments, particularly in urban centers like Addis Ababa.
Overall, Ethiopia’s infrastructure development efforts have been instrumental in driving economic growth and improving the quality of life for its citizens. The government’s commitment to investing in various sectors, such as transportation, energy, telecommunications, water supply, and housing, has positioned Ethiopia as one of the fastest-growing economies in Africa.
Why Infrastructures matter
play a crucial role in the development and progress of any country, including Ethiopia. The presence of well-developed and efficient infrastructures is essential for various reasons, ranging from economic growth and social development to improved living standards and enhanced connectivity.
One of the primary reasons why infrastructures matter in Ethiopia is their contribution to economic growth. Investments in infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, airports, ports, and energy facilities can stimulate economic activities by facilitating the movement of goods, services, and people. Improved transportation networks enable businesses to transport their products more efficiently, reducing costs and increasing competitiveness. Additionally, reliable energy infrastructure ensures uninterrupted power supply, which is vital for industrial production and attracting foreign investments.
Furthermore, infrastructures are crucial for poverty reduction and social development in Ethiopia. Access to basic amenities such as clean water, sanitation facilities, healthcare centers, and educational institutions is essential for improving the quality of life for the population. Well-developed infrastructures in these sectors ensure that essential services are accessible to all citizens, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status. For instance, the construction of schools and hospitals in rural areas can significantly improve access to education and healthcare for marginalized communities.
Moreover, infrastructures contribute to regional integration and connectivity within Ethiopia. Efficient transportation networks connect different regions of the country, promoting trade and commerce between urban centers and rural areas. This connectivity not only fosters economic growth but also enhances social cohesion by reducing regional disparities. Additionally, well-connected infrastructures facilitate the movement of people within the country, enabling individuals to access employment opportunities, education, healthcare services, and cultural exchanges.
In addition to these reasons, infrastructures also play a vital role in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) into Ethiopia. Investors often consider the quality of a country’s infrastructure when deciding where to invest their capital. A well-developed infrastructure network provides a favorable business environment, as it ensures efficient logistics, reduces operational costs, and enhances connectivity with global markets. Therefore, by investing in infrastructures, Ethiopia can attract more FDI, which can further stimulate economic growth and create employment opportunities.
In conclusion, infrastructures are of utmost importance in Ethiopia due to their significant impact on economic growth, social development, regional integration, and connectivity. By investing in well-developed and efficient infrastructures, Ethiopia can foster sustainable development, improve living standards, reduce poverty, and attract foreign investments.