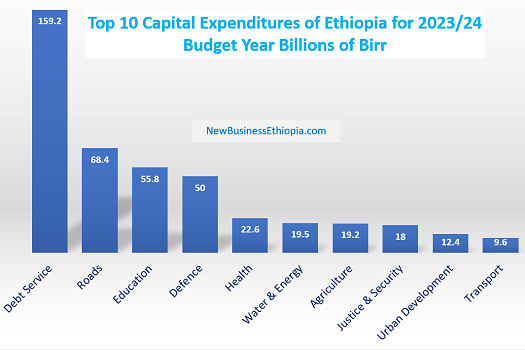
For two consecutive years, debt service continues to be the highest budgetary line item, absorbing 159 billion Birr, up 26 percent from last year’s budget (2022/23), while defense budget is down 40 percent.
This is shown in the latest 802 billion Birr total annual budget document of the country for the 2016 Ethiopian fiscal year – 2023/24 (July 8, 2023 to July 7, 2024) – approved by the House of Peoples Representatives a few weeks ago. “The share of expenditure on poverty-reduction (mainly in education, health, road etc), has continued to decline, at 57 percent of the total expenditure versus the 75 percent share five years ago. This partly reflects the rising share of spending allocated to covering debt repayments and the priority given to covering such outstanding obligations,” stated the budget report made by Cepheus Capital.
Meanwhile, Ethiopia’s public debt-to-GDP ratio stood at 39 percent at the end of March 2023, which is far below the average of 66 percent for African countries and 69 percent for emerging markets, according to the report. “This indicates that Ethiopia’s debt burden is relatively manageable. However, the debt service to exports ratio (77 percent versus SSA of 20 percent) and the debt service to revenue ratio (31 percent versus Sub-Saharan Africa of 17 percent) are both high, given the country’s still low export and revenue base,” stated the report.”
The other areas with highest growth rates in budgetary spending were in allocations for trade and industry (up 23 percent), transport and communication (up 20 percent), agriculture (up 17 percent), and health (up 17 percent).
On the contrary, this year’s defense budget of Ethiopia has shown a decline of 40 percent, or from last year’s 84 billion Birr to 50 billion Birr, as spending shifts to reconstruction and development activities. Other line items that have shown a decline in growth include Urban Development and Construction, education, water resource and energy, and mining.
In relation to budget deficit, the deficit of 281 billion birr (around 2.4 percent of GDP) for the budget year 2023/24 will be covered mostly from domestic borrowing (86 percent of the total financing). The foreign funding of 39 billion Birr (0.3 percent of GDP) is among the lowest levels seen in recent years, and compares to a high seen in 2019/20, when 70 percent of the budget was covered by external financing, according to Cepheus Research on Ethiopia’s budget released a few days ago.
The Ethiopian Government is anticipating budgetary grants of 41 billion Birr (around $770 million) with the sources of these grants mainly being the World Bank, the EU, the AfDB, the UK, and the US. The Government is also expecting external budgetary borrowing of 39 billion Birr (around $731 million) in the 2023/24 fiscal year. The majority of these borrowings are expected to come from the World Bank, with some limited bilateral loans from countries such as China, Saudi Arabia, and Italy, according to Cepheus report.