BEHAK Exclusive – Ethiopia holds the largest cattle population from Africa which has estimated to be about 70 million heads of cattle. Out of total cattle population, the female cattle constitute about 56 percent and the remaining 44 percent are male. About 97.4% of the total cattle in the country are local breeds. The remaining are hybrid and exotic breeds that accounted for about 2.3 percent and 0.31 percent, respectively and there are milking cows are about 15.04 million heads. In 2020/21, there was 4.96 billion liters of cow milk produced per year in the country.
The dairy products market in Ethiopia has been experiencing significant growth in recent years though per capita consumption of milk is approximately 19 kg per year in Ethiopia, lower than the 30.2 kg/year of Sub-Saharan average. The country’s dairy industry plays a crucial role in the economy, providing employment opportunities and contributing to the overall food security of the nation. Dairy products are an essential part of the Ethiopian diet, and their consumption is increasing as the population grows and incomes rise.
Ethiopia’s dairy sector is primarily composed of small-scale farmers, who account for the majority of milk production in the country. These farmers typically own a few cows or goats and produce milk for household consumption or local markets. However, there are also larger commercial dairy farms that have emerged in recent years, aiming to meet the growing demand for dairy products.
One of the main challenges faced by the Ethiopian dairy industry is low productivity. Small-scale farmers often lack access to modern farming techniques, quality animal feed, and veterinary services. This leads to lower milk yields and limits the potential for growth in the sector. Efforts are being made by both the government and various organizations to address these challenges through training programs, improved access to inputs, and better extension services.
The demand for dairy products in Ethiopia has been increasing steadily, driven by factors such as population growth, urbanization, and changing dietary preferences. Milk and other dairy products are considered nutritious and are an important source of protein, vitamins, and minerals. As people’s incomes rise, they tend to consume more dairy products as part of a diversified diet.
In terms of consumption patterns, liquid milk is the most commonly consumed dairy product in Ethiopia. It is consumed both in its raw form and processed into traditional products such as ayib (cottage cheese) and ergo (fermented milk). Other popular dairy products include butter, ghee, yogurt, and cheese.
Manufacturing
Dairy product manufacturing in Ethiopia has been gaining significant attention and growth in recent years. The country’s dairy industry plays a crucial role in providing employment opportunities, contributing to the national economy, and meeting the nutritional needs of its population. This comprehensive response will delve into various aspects of the manufacturing of dairy products in Ethiopia, including production, processing, challenges, and future prospects.
Production of Milk
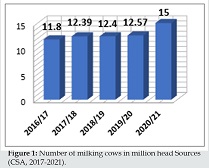
Ethiopia has a substantial livestock population, which forms the foundation for milk production. The country is known for its large number of cattle, sheep, and goats, which are the primary sources of milk. According to the Central Statistical Agency (CSA) of Ethiopia, the total livestock population in 2019/2020 was estimated at around 60 million cattle, 30 million sheep, and 30 million goats.
Milk production in Ethiopia is predominantly carried out by smallholder farmers who own a few animals. These farmers play a vital role in supplying raw milk to the dairy industry. However, despite the large livestock population, milk productivity per animal remains relatively low due to various factors such as poor feeding practices, limited access to veterinary services, and inadequate infrastructure.
Processing of Milk
The processing of milk into various dairy products is an essential step in the dairy industry. In Ethiopia, there are both formal and informal milk processing systems. The formal sector consists of large-scale dairy processing companies that adhere to quality standards and regulations set by the government. These companies produce a wide range of dairy products such as pasteurized milk, yogurt, cheese, butter, and ice cream.
On the other hand, the informal sector comprises small-scale processors who often operate at a household or community level. They produce traditional dairy products like ayib (Ethiopian cottage cheese) and ergo (Ethiopian butter). While these informal processors may not always meet formal quality standards, they play a significant role in meeting local demand and preserving traditional dairy processing practices.
Challenges
The manufacturing of dairy products in Ethiopia faces several challenges that hinder its growth and development. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Low milk productivity: The average milk yield per animal in Ethiopia is relatively low compared to other countries. This can be attributed to factors such as inadequate feeding practices, limited access to improved breeds, and poor animal health management.
2. Lack of infrastructure: The dairy industry in Ethiopia lacks adequate infrastructure, including milk collection centers, cold storage facilities, and transportation networks. This hampers the efficient collection and distribution of milk, leading to spoilage and quality deterioration.
3. Limited access to finance: Smallholder farmers and small-scale processors often face difficulties in accessing finance for investment in dairy production and processing. This limits their ability to adopt modern technologies, improve productivity, and expand their operations.
4. Quality control: Ensuring consistent quality control throughout the dairy value chain remains a challenge in Ethiopia. There is a need for improved testing facilities, training programs for farmers and processors, and stricter enforcement of quality standards.
Top Ten Companies Engaged in Dairy Products in Ethiopia
Ethiopia has a growing dairy industry, with several major companies engaged in the production and processing of dairy products. These companies play a significant role in meeting the domestic demand for dairy products and contribute to the country’s economy. Here are some of the major companies engaged in dairy products in Ethiopia:
1. Faffa Food Share Company: Faffa Food is one of the leading dairy companies in Ethiopia. It was established in 1992 and has since become a prominent player in the dairy industry. Faffa Food operates a modern dairy farm and processing plant located in Sululta, near Addis Ababa. The company produces a wide range of dairy products, including milk, yogurt, cheese, butter, and ice cream. Faffa Food focuses on maintaining high-quality standards and has gained a strong reputation for its products.
2. Lemlem Dairy: Lemlem Dairy is another major player in Ethiopia’s dairy industry. Founded in 2006, the company operates a large-scale dairy farm and processing facility in Holeta, Oromia region. Lemlem Dairy specializes in producing pasteurized milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter. The company follows international quality standards and employs modern technology to ensure the freshness and safety of its products.
3. Milkman Dairy: Milkman Dairy is a well-known name in Ethiopia’s dairy sector. Established in 2010, the company operates a state-of-the-art dairy farm and processing plant in Bishoftu town, Oromia region. Milkman Dairy focuses on producing high-quality milk and milk-based products such as yogurt, cheese, and butter. The company emphasizes sustainable farming practices and animal welfare.
4. Guteta Dairy: Guteta Dairy is a prominent Ethiopian company engaged in the production of dairy products. Founded in 2004, the company operates a modern dairy farm and processing facility in Debre Zeit, Oromia region. Guteta Dairy produces a wide range of dairy products, including milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter. The company is known for its commitment to quality and has gained a significant market share in Ethiopia.
5. Addis Ababa Milk and Milk Products Processing Factory: Addis Ababa Milk Factory is a state-owned enterprise that plays a crucial role in Ethiopia’s dairy industry. Established in 1979, the factory is located in Addis Ababa and produces various dairy products, including pasteurized milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter. The factory aims to meet the growing demand for dairy products in the capital city and surrounding areas.
6. Ethio-Danish Dairy Production and Marketing Share Company: Ethio-Danish Dairy is a joint venture between Ethiopian and Danish investors. The company operates a large-scale dairy farm and processing plant in Bishoftu town, Oromia region. Ethio-Danish Dairy focuses on producing high-quality milk and milk-based products for both domestic and international markets.
7. Bokra Dairy: Bokra Dairy is an emerging player in Ethiopia’s dairy industry. The company operates a modern dairy farm and processing facility in Sululta, near Addis Ababa. Bokra Dairy produces various dairy products, including milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter. The company aims to contribute to the development of the local dairy sector by providing high-quality products.
8. Holland Dairy: Holland Dairy is a leading provider of high-quality dairy products mainly yoghurt and milk in the entire country of Ethiopia.
9. Gebeta Dairy: Gebeta Dairy is a well-established dairy company that operates in Ethiopia. It produces various dairy products such as milk, yogurt, butter, and cheese. Gebeta Dairy has a strong distribution network across the country, making its products easily accessible to consumers.
10. Birhan Dairy: Birhan Dairy is a relatively new player in the Ethiopian dairy industry but has quickly gained recognition for its high-quality dairy products. The company focuses on producing and distributing milk, yogurt, and other dairy products.
Future Prospects
Despite the challenges, the manufacturing of dairy products in Ethiopia holds promising prospects for the future. The government has recognized the importance of the dairy sector and has implemented various initiatives to support its growth. These include:
1. Investment incentives: The Ethiopian government offers various incentives to attract domestic and foreign investments in the dairy sector. These incentives include tax breaks, access to land, and financial support for infrastructure development.
2. Capacity building: Efforts are being made to enhance the capacity of smallholder farmers and processors through training programs on improved animal husbandry practices, feed management, and modern processing techniques.
3. Market development: The government is working towards expanding domestic and international markets for Ethiopian dairy products. This includes promoting exports through trade agreements, improving product quality, and enhancing marketing and branding efforts.
Furthermore, there is an increasing demand for dairy products in Ethiopia due to population growth, urbanization, and changing dietary patterns. This presents opportunities for both large-scale and small-scale dairy processors to meet the growing consumer demand.
Imported Dairy Products
Due to various factors such as limited land availability for grazing and low milk productivity, Ethiopia relies on imports to meet the growing demand for dairy products.
The country’s growing urban population, changing dietary patterns, and increasing disposable income have led to a rise in demand for processed dairy products such as milk powder, butter, cheese, and yogurt. Importing these products helps meet consumer demand and ensures a stable supply of dairy products in the market.
Types of Dairy Products Imported:
Ethiopia imports various types of dairy products to fulfill its domestic demand. These include:
1. Milk Powder: Milk powder is one of the most commonly imported dairy products in Ethiopia. It is used for various purposes such as reconstitution into liquid milk, production of infant formula, and as an ingredient in the food processing industry.
2. Butter: Butter is another significant dairy product imported by Ethiopia. It is used both for household consumption and in the food service sector.
3. Cheese: Cheese imports have also seen a steady increase in recent years. Different types of cheese are imported to cater to the diverse preferences of consumers.
4. Yogurt: Yogurt imports have gained popularity due to the increasing awareness of its health benefits. Different flavors and varieties of yogurt are imported to meet consumer demand.
Reasons for Dairy Imports:
There are several reasons why Ethiopia relies on dairy imports:
1. Insufficient Domestic Production: The domestic dairy industry in Ethiopia faces challenges such as low milk productivity, limited access to improved breeds, and inadequate veterinary services. These factors contribute to insufficient domestic production, leading to a reliance on imports.
2. Growing Urban Population: Ethiopia’s urban population is growing rapidly, leading to an increased demand for dairy products. The domestic production alone cannot meet this rising demand, necessitating imports.
3. Changing Dietary Patterns: As incomes rise and lifestyles change, there is a shift in dietary patterns towards processed and convenience foods. This includes an increased consumption of dairy products, which cannot be met solely by domestic production.
4. Market Demand for Variety: Consumers in Ethiopia have diverse preferences when it comes to dairy products. Importing a wide range of products allows the market to cater to these preferences and provide consumers with a variety of choices.
Government Initiatives and Policies:
The Ethiopian government has recognized the importance of the dairy sector and has implemented various initiatives and policies to promote domestic production and reduce reliance on imports. These include:
1. Livestock Development Strategy: The government has developed a Livestock Development Strategy that aims to improve the productivity and competitiveness of the livestock sector, including the dairy sub-sector. This strategy focuses on improving animal health services, promoting breed improvement programs, and enhancing market access for smallholder farmers.
2. Investment Incentives: The government provides investment incentives for both local and foreign investors interested in the dairy sector. These incentives include tax breaks, access to credit facilities, and support for technology transfer.
3. Capacity Building: The government has also invested in capacity building programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of dairy farmers and other stakeholders in the sector. This includes training programs on improved animal husbandry practices, milk quality control, and value addition.
In general, to meet the growing demand for milk in Ethiopia, milk production has to grow at least at a rate of 4% per annum, according to the June 2022 study by Ararsa Gutema Kula. Despite the growth potential, the dairy industry in Ethiopia faces several challenges. Limited access to modern technology and improved breeding practices hinders productivity and milk yields. Inadequate infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities and transportation networks, affects the quality and shelf life of dairy products. Additionally, the lack of skilled manpower and technical expertise poses challenges in terms of processing and value addition.
In conclusion, the market size of dairy products in Ethiopia is influenced by population growth, economic development, consumer preferences, and government policies. With a large population and increasing disposable income, there is a growing demand for dairy products in Ethiopia. However, challenges such as limited access to technology and infrastructure need to be addressed to fully unlock the potential of the dairy industry.

