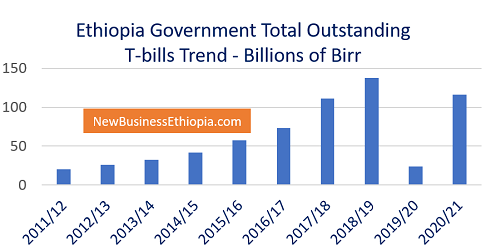
Ethiopia’s Government total outstanding treasury bills (T-bills) has increased by close to 500 percent in 2020/21 to 116.6 billion Birr compared to the previous year.
At the end of the year 2019/20 ended June 30, 2020, the total T-bills of Ethiopia was about 23.7 billion Birr, according to the official statistics from the National Bank of Ethiopia (NBE). “This was mainly attributed to the policy change on the issuance of T-bills since December 2019,” the annual report of NBE released last month (March 2022) stated.
Treasury bill is often auctioned by governments when they run out of cash and or finance critical development projects. It is a short-term debt issued by governments and considered as the money the governments owe to the institutions that bought T-bills.
The report stated that commercial banks’ participation in T-bill auction market has shown significant improvement and “accounted for 52.0 billion Birr or 44.6% of the total outstanding T-Bills where that of non-bank institutions stood at 64.5 billion Birr or 55.4 %”.
Average weighted yield of all types of T-bills increased to almost 8 percent from around 4.5 percent during the review period (2020/21).
“The highest yield was recorded for the 364-day T-bills and the lowest 28- day T-bills with a corresponding yield rate of 9.032 and 6.826 percent, respectively.”
The total T-bills offered to the T-bills auction market in 2020/21 showed a 42.9 percent increment and reached 330.7 billion Birr while demand for T-bills increased 17.1 percent to reach 284.8 billion Birr.
“This indicated that the market was undersubscribed by 45.9 billion Birr (13.9 percent). Thus, the number of T-bills sold during the fiscal year was 238.8 billion Birr which was lower than the demand by 46 billion Birr,” NBE’s report stated.