BEHAK Exclusive – Ethiopia (126.8 USD billion GDP, and about 123 million population in 2022) and India ($3.75 trillion GDP, and 1.42 billion population in 2022) have a long-standing trade relationship that dates back centuries. The trade ties between the two countries have been characterized by mutual cooperation and economic exchanges in various sectors. This comprehensive analysis will explore the historical background, key sectors of trade and top twenty products traded, bilateral agreements, and future prospects of the Ethiopia-India trade relationship.
Historical ties
The trade relationship between Ethiopia and India can be traced back to ancient times when maritime trade routes connected the Indian subcontinent with the Horn of Africa. Historical records indicate that Indian traders, particularly from the southern state of Kerala, had established commercial links with the Ethiopian port city of Adulis as early as the 1st century AD. These early interactions laid the foundation for a long-lasting trade relationship between the two regions.
Trade Relation
Ethiopia and India have a long history of trade relations that date back centuries. The trade between these two countries has been mutually beneficial, contributing to economic growth and development in both nations. In recent years, the trade volume between Ethiopia and India has witnessed significant growth, with a diverse range of goods being exchanged.
Ethiopia and India have maintained diplomatic relations since the establishment of the Ethiopian Embassy in New Delhi in 1948. Over the years, these relations have expanded to encompass various sectors, including trade and investment. Both countries have taken steps to enhance bilateral trade by signing agreements and establishing mechanisms for cooperation.
Trade Volume
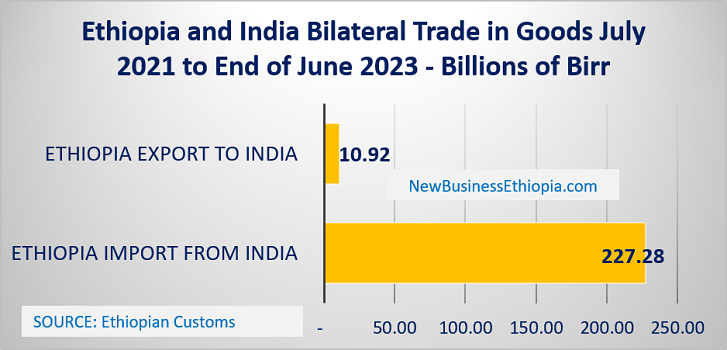
The trade volume between Ethiopia and India has been steadily increasing over the past decade. According to data from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of India, the total bilateral trade between the two countries reached USD 1.27 billion in 2019-2020. This represents a significant increase from previous years, highlighting the growing economic ties between Ethiopia and India.
Exports from Ethiopia to India
Ethiopia primarily exports agricultural products, minerals, and textiles to India. Coffee is one of the major exports from Ethiopia to India, as Indian consumers have a strong demand for Ethiopian coffee beans. Other agricultural products exported from Ethiopia to India include oilseeds, pulses, spices, and fruits. Additionally, Ethiopia exports minerals such as gold and tantalum to India. Textiles and garments are also significant exports from Ethiopia to India.
Top 20 products Ethiopia Export to India
Ethiopia is known for its diverse range of exports, including agricultural products, textiles, and minerals. When it comes to trade with India, Ethiopia exports various goods that cater to India’s demand for raw materials, agricultural products, and manufactured goods. While the specific rankings may vary over time, here is a comprehensive list of the top 20 goods that Ethiopia exports to India:
1. Coffee: Ethiopia is renowned for its high-quality coffee beans, and it is one of the largest exporters of coffee in the world. Indian consumers have a strong affinity for Ethiopian coffee due to its unique flavor profiles.
2. Oilseeds: Ethiopia exports various oilseeds such as sesame seeds, niger seeds, and linseeds to India. These oilseeds are used in the production of cooking oils and other food products.
3. Pulses: Pulses like chickpeas, lentils, and pigeon peas are major exports from Ethiopia to India. These pulses are an essential ingredient in Indian cuisine and are in high demand.
4. Spices: Ethiopia exports a variety of spices to India, including black cumin seeds, coriander seeds, and fenugreek seeds. These spices are widely used in Indian cooking and contribute to the rich flavors of Indian dishes.
5. Textiles: Ethiopia has a growing textile industry and exports various textile products such as cotton yarn, fabrics, and garments to India. Indian manufacturers often import these textiles for further processing or distribution.
6. Leather Products: Ethiopia is known for its high-quality leather products such as shoes, bags, and accessories. Indian consumers have a preference for Ethiopian leather goods due to their durability and craftsmanship.
7. Gems and Jewelry: Ethiopia has significant deposits of precious gemstones like opals and emeralds. These gemstones are exported to India’s jewelry industry for cutting, polishing, and manufacturing.
8. Minerals: Ethiopia exports minerals like tantalum, gold, and gemstones to India. These minerals are used in various industries, including electronics, jewelry, and manufacturing.
9. Sisal Fiber: Sisal fiber is a natural fiber extracted from the leaves of the sisal plant. Ethiopia exports sisal fiber to India, where it is used in the production of ropes, twines, and other fiber-based products.
10. Sesame Oil: Ethiopia is a major exporter of sesame oil to India. Sesame oil is widely used in Indian cooking and is known for its distinct flavor and health benefits.
11. Tea: Although India is famous for its tea production, Ethiopia also exports tea to India. Ethiopian tea is known for its unique flavors and is often blended with Indian teas.
12. Hides and Skins: Ethiopia exports hides and skins to India’s leather industry for further processing and manufacturing of leather products.
13. Cereals: Cereals like maize (corn), wheat, and barley are exported from Ethiopia to India. These cereals are used as food grains or as raw materials in various industries.
14. Poultry Products: Ethiopia exports poultry products such as chicken meat and eggs to India. These products cater to the growing demand for poultry in the Indian market.
15. Fruits and Vegetables: Ethiopia exports a variety of fruits and vegetables to India, including mangoes, avocados, bananas, and beans. These fresh produce items are in high demand due to their quality and taste.
16. Petrochemicals: Ethiopia exports petrochemical products like petroleum oils, bitumen, and other related products to India’s industrial sector.
17. Wood Products: Ethiopia exports wood products such as sawn timber, plywood, and furniture to India’s construction and furniture industries.
18. Cotton: Ethiopia exports raw cotton to India, which is used in the textile industry for the production of fabrics and garments.
19. Pulp and Paper: Ethiopia exports pulp and paper products to India, which are used in various industries such as printing, packaging, and stationery.
20. Electrical Machinery: Ethiopia exports electrical machinery and equipment to India, including generators, transformers, and electrical parts.
These are some of the top goods that Ethiopia exports to India. It is important to note that the rankings may vary over time due to changes in demand and market conditions.
Imports from India to Ethiopia
India is a major supplier of various goods to Ethiopia. Some of the key imports from India include pharmaceuticals, machinery, vehicles, iron and steel products, chemicals, textiles, and electronics. Indian pharmaceutical companies have a strong presence in Ethiopia and supply a significant portion of the country’s pharmaceutical needs. Indian machinery and vehicles are also popular imports in Ethiopia due to their quality and competitive pricing.
Top 20 Products India Exports to Ethiopia
India exports a wide range of products to Ethiopia, contributing to the economic development of both nations. The top 20 products that India exports to Ethiopia include:
1. Pharmaceuticals: India is known for its robust pharmaceutical industry and exports a significant amount of pharmaceutical products to Ethiopia. These include medicines, vaccines, and other healthcare products.
2. Textiles and garments: India is a leading exporter of textiles and garments globally. Ethiopian consumers have a high demand for Indian textiles, including cotton fabrics, silk fabrics, and ready-made garments.
3. Machinery and equipment: India exports various types of machinery and equipment to Ethiopia, including agricultural machinery, construction machinery, industrial machinery, and electrical equipment.
4. Iron and steel products: India is a major producer of iron and steel products and exports these commodities to Ethiopia. This includes iron ore, steel bars, pipes, sheets, and other related products.
5. Automobiles and spare parts: Indian automobile manufacturers export vehicles and spare parts to Ethiopia. This includes cars, motorcycles, tractors, and components such as engines, tires, batteries, and electrical parts.
6. Chemicals: India exports a wide range of chemicals to Ethiopia, including organic chemicals, inorganic chemicals, dyes, pigments, fertilizers, and pharmaceutical intermediates.
7. Plastic products: Indian plastic manufacturers export various plastic products to Ethiopia. This includes plastic packaging materials, containers, bags, pipes, fittings, and household items.
8. Electronics: India is a major exporter of electronic goods to Ethiopia. This includes consumer electronics such as televisions, refrigerators, air conditioners, mobile phones, as well as electronic components.
9. Leather products: Indian leather manufacturers export leather goods such as shoes, bags, belts, and wallets to Ethiopia. India is known for its high-quality leather products.
10. Cosmetics and personal care products: Indian cosmetic companies export a range of beauty and personal care products to Ethiopia. This includes skincare products, hair care products, cosmetics, and perfumes.
11. Food products: India exports various food products to Ethiopia, including rice, wheat flour, spices, tea, coffee, pulses, edible oils, and processed foods.
12. Paper and paper products: Indian paper manufacturers export paper and paper products to Ethiopia. This includes printing paper, packaging materials, notebooks, and stationery items.
13. Rubber products: India exports rubber products such as tires, tubes, hoses, gaskets, and seals to Ethiopia. These are used in various industries including automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
14. Ceramic products: Indian ceramic manufacturers export ceramic tiles, sanitaryware, tableware, and other ceramic products to Ethiopia.
15. Jewelry: India is renowned for its jewelry industry and exports gold and diamond jewelry to Ethiopia. Indian jewelry is highly valued for its craftsmanship and design.
16. Handicrafts: Indian artisans produce a wide range of handicrafts including wooden crafts, metal crafts, textiles, pottery, and jewelry. These handicrafts are exported to Ethiopia.
17. Electrical appliances: India exports electrical appliances such as fans, lighting fixtures, switches, sockets, and cables to Ethiopia.
18. Construction materials: India exports construction materials such as cement, steel bars, tiles, glass sheets, and sanitary fittings to Ethiopia.
19. Furniture: Indian furniture manufacturers export a variety of furniture items including wooden furniture, metal furniture, plastic furniture, and office furniture to Ethiopia.
20. Sports goods: India is a major exporter of sports goods including cricket equipment, footballs, tennis rackets, badminton rackets, and other sports accessories to Ethiopia.
Key Sectors of Trade
1. Agriculture: Agriculture is a significant sector in both Ethiopia and India, and it plays a crucial role in their bilateral trade. India has been a major importer of Ethiopian agricultural products such as coffee, oilseeds, pulses, spices, and sesame seeds. On the other hand, Ethiopia imports Indian agricultural machinery, fertilizers, and hybrid seeds to enhance its agricultural productivity.
2. Textiles and Garments: The textile industry is another important sector in the Ethiopia-India trade relationship. Indian textile companies have invested in Ethiopia’s textile and garment manufacturing sector due to its favorable investment climate and low labor costs. These investments have led to an increase in exports of textiles and garments from Ethiopia to India.
3. Pharmaceuticals: India is known globally for its pharmaceutical industry, which produces high-quality generic drugs at affordable prices. Ethiopian pharmaceutical companies import a significant portion of their raw materials and finished products from India. This collaboration has helped improve access to affordable healthcare in Ethiopia.
4. Information Technology: India is renowned for its IT industry, and Ethiopian companies have increasingly sought partnerships with Indian IT firms to enhance their technological capabilities. Indian IT companies have been involved in various projects in Ethiopia, including the development of e-governance systems, software development, and capacity building initiatives.
5. Education and Skill Development: India has been providing scholarships and training opportunities to Ethiopian students and professionals in various fields such as medicine, engineering, agriculture, and information technology. This collaboration has contributed to the human resource development of Ethiopia and strengthened the bilateral ties between the two countries.
Bilateral Agreements
Ethiopia and India have signed several bilateral agreements to promote trade and investment between the two countries. Some notable agreements include:
1. Bilateral Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement (BIPPA): Signed in 2007, this agreement aims to provide a conducive environment for investment by ensuring fair treatment, protection, and security of investments made by investors from both countries.
2. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA): The DTAA signed between Ethiopia and India helps prevent double taxation on income earned by residents of one country in the other country. This agreement provides clarity on tax liabilities and promotes cross-border trade and investment.
3. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on Cooperation in the Field of Agriculture: Signed in 2011, this MoU focuses on enhancing cooperation in agricultural research, technology transfer, capacity building, and exchange of agricultural experts between Ethiopia and India.
Investment and Joint Ventures
In addition to trade, India has also made significant investments in Ethiopia. Indian companies have established joint ventures and invested in various sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and information technology. We will analyse these investments in another article.
Government Initiatives
Both the Ethiopian and Indian governments have taken steps to further enhance trade relations between the two countries. In 2011, the India-Ethiopia Joint Trade Committee was established to promote bilateral trade and investment. The committee meets regularly to discuss issues related to trade facilitation, market access, and investment promotion. Additionally, both countries have signed agreements on double taxation avoidance and the promotion and protection of investments.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the trade relations between Ethiopia and India have been growing steadily, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. These include logistical constraints, such as limited air connectivity and high transportation costs. Additionally, trade barriers such as tariffs and non-tariff barriers can hinder the growth of bilateral trade. However, there are also significant opportunities for further collaboration, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, renewable energy, and information technology.
Overall, the trade relations between Ethiopia and India have witnessed substantial growth in recent years. Both countries have recognized the importance of enhancing bilateral trade and have taken steps to promote economic cooperation. With a diverse range of goods being exchanged, there is immense potential for further expansion of trade between Ethiopia and India.
Future Prospects
The trade relationship between Ethiopia and India is expected to further strengthen in the coming years. Both countries have recognized the potential for increased economic cooperation and have taken steps to facilitate trade and investment. Some key areas of focus for future collaboration include:
1. Infrastructure Development: India has expressed interest in investing in Ethiopia’s infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, power generation, and industrial parks. These investments would not only boost Ethiopia’s infrastructure development but also create opportunities for Indian companies to participate in large-scale projects.
2. Manufacturing and Industrialization: Ethiopia aims to become a manufacturing hub in Africa, and India can play a significant role in supporting this objective. Indian companies have already invested in sectors such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, and automotive components. Further collaboration in manufacturing and industrialization can lead to job creation, technology transfer, and export diversification.
3. Renewable Energy: Both Ethiopia and India have made significant strides in renewable energy development. Ethiopia has abundant renewable energy resources, particularly hydroelectric power, while India has expertise in solar and wind energy. Collaboration in the renewable energy sector can help Ethiopia meet its growing energy demands sustainably.
In conclusion, the trade relationship between Ethiopia and India is multifaceted and encompasses various sectors such as agriculture, textiles, pharmaceuticals, information technology, and education. The historical ties between the two countries have laid a strong foundation for economic cooperation. Bilateral agreements and future prospects indicate that the trade relationship is poised to grow further, benefiting both nations.