BEHAK Exclusive – Ethiopia and China have a significant trade relationship, with the trade volume between the two countries steadily increasing over the years. This trade partnership has been mutually beneficial, contributing to economic growth and development in both nations. In this article we look into the volume of growing trade between the two countries, the major traded commodities, the factors contributing to the growth, the challenges and opportunities.
The trade volume between Ethiopia and China has experienced substantial growth in recent years.
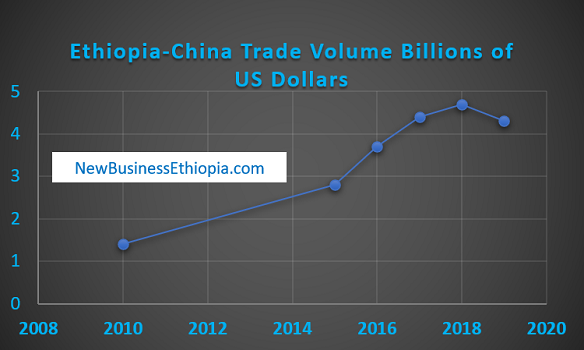
Trade Volume Trends
From 2010 to 2019, Ethiopia’s trade volume with China witnessed substantial growth. This can be attributed to various factors such as increased bilateral agreements, infrastructure development projects, and growing demand for Ethiopian commodities in the Chinese market.
In 2010, the total trade volume between Ethiopia and China was recorded at approximately $1.4 billion. Over the next few years, this figure experienced consistent growth. By 2015, the trade volume had reached around $2.8 billion, indicating a significant increase in bilateral trade activities.
The subsequent years saw even more remarkable growth in trade volume. In 2016, it reached approximately $3.7 billion, followed by a further increase to around $4.4 billion in 2017. The upward trend continued in 2018 when the trade volume reached approximately $4.7 billion.
However, in 2019, there was a slight decline in the trade volume between Ethiopia and China due to various factors such as global economic uncertainties and domestic challenges faced by both countries. The total trade volume for that year was recorded at approximately $4.3 billion.
Ethiopia’s export to China
Ethiopia’s export commodities to China in USD have experienced significant growth over the years. Ethiopia’s exports to China amounted to approximately $1.2 billion in 2019, according to the latest available data.
One of the key export commodities from Ethiopia to China is coffee. Ethiopia is known for its high-quality coffee production, and China has emerged as a major market for Ethiopian coffee beans. The demand for Ethiopian coffee in China has been steadily increasing due to factors such as rising disposable incomes, changing consumer preferences, and the growing popularity of coffee consumption in China. Coffee exports from Ethiopia to China have contributed significantly to the overall export revenue.
Another significant export commodity from Ethiopia to China is oilseeds. Ethiopia is one of the largest producers of oilseeds in Africa, and China has become a major importer of Ethiopian oilseeds. The main oilseed crops exported from Ethiopia to China include sesame seeds, linseeds, and Niger seeds. These oilseeds are used in various industries such as food processing, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals in China.
Textiles and garments also form a notable portion of Ethiopia’s exports to China. The Ethiopian textile and garment industry has been growing rapidly in recent years, attracting investments from Chinese companies. Chinese manufacturers have set up textile factories in Ethiopia, taking advantage of the country’s low labor costs and preferential trade agreements with Western markets. As a result, Ethiopia has been exporting an increasing amount of textiles and garments to China.
In addition to these key commodities, other export products from Ethiopia to China include leather and leather products, minerals, fruits, vegetables, and spices. These products contribute to the overall export revenue and bilateral trade between the two countries.
The Reasons
One of the key factors contributing to this growth is Ethiopia’s focus on exporting primary commodities such as agricultural products and raw materials to China. Ethiopia is known for its production of coffee, oilseeds, pulses, and leather products, which are in high demand in the Chinese market. These commodities accounted for a significant portion of Ethiopia’s exports to China.
Furthermore, Ethiopia has been actively promoting investment and trade relations with China through various initiatives. The Chinese government has provided financial support and technical assistance to Ethiopia, enabling the country to develop its infrastructure and industrial sectors. This has created opportunities for Ethiopian businesses to expand their export capabilities and cater to the Chinese market.
In recent years, there has also been an increase in the export of manufactured goods from Ethiopia to China. The Ethiopian government has implemented policies aimed at attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in sectors such as textiles and garments, footwear, and electronics. As a result, Chinese companies have set up manufacturing facilities in Ethiopia to take advantage of the country’s low labor costs and preferential trade agreements.
Additionally, Ethiopia’s participation in international trade fairs and exhibitions organized by China has helped promote its products and attract Chinese buyers. These events provide a platform for Ethiopian exporters to showcase their goods and establish business contacts with potential Chinese partners.
China’s Export to Ethiopia
China’s export value to Ethiopia has been steadily increasing over the years. Ethiopia is one of China’s major trading partners in Africa, and the bilateral trade between the two countries has witnessed significant growth.
China’s export value to Ethiopia reached $2.84 billion in 2019, according to the latest available data. This marked a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting the strengthening economic ties between the two nations. It is worth noting that this figure represents only the official recorded exports and does not account for informal or unrecorded trade.
China exports a wide range of products to Ethiopia, including machinery, electronics, textiles, garments, vehicles, and construction materials. These goods cater to various sectors of Ethiopia’s economy, such as infrastructure development, manufacturing, and consumer goods.
China’s major export commodities to Ethiopia include:
1. Machinery and Electrical Equipment: China is known for its manufacturing capabilities, and machinery and electrical equipment are among its top exports to Ethiopia. This category includes items such as machinery parts, generators, electrical appliances, and telecommunications equipment.
2. Textiles and Apparel: China is one of the largest producers of textiles and apparel globally. It exports a significant amount of clothing, fabrics, and accessories to Ethiopia. Chinese textiles are often competitively priced, making them popular in the Ethiopian market.
3. Vehicles and Automotive Parts: China has a growing automotive industry and exports vehicles and automotive parts to various countries, including Ethiopia. This category includes passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, and spare parts.
4. Construction Materials: China is also a major exporter of construction materials to Ethiopia. This includes products like steel bars, cement, glass, tiles, and other building materials.
5. Chemical Products: China exports various chemical products to Ethiopia, including fertilizers, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and synthetic fibers.
6. Consumer Electronics: Chinese-made consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, and home appliances are also exported to Ethiopia.
7. Furniture: China is known for its furniture manufacturing industry and exports a range of furniture products to Ethiopia.
8. Plastic Products: China is a significant exporter of plastic products to Ethiopia, including packaging materials, household items, and industrial plastics.
9. Footwear: Chinese-made footwear products are also exported to Ethiopia.
10. Agricultural Machinery and Equipment: China exports agricultural machinery and equipment such as tractors, irrigation systems, harvesters, and other farming tools to Ethiopia.
Factors
The growth in China’s export value to Ethiopia can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, China has become a global manufacturing hub and offers competitive prices for its products. This makes Chinese goods attractive to Ethiopian importers who seek affordable options.
Secondly, China has actively pursued economic cooperation with African countries through initiatives like the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC). This has led to increased investment and trade between China and Ethiopia, resulting in a boost in export value.
Furthermore, Chinese companies have been involved in numerous infrastructure projects in Ethiopia, such as road construction, railway development, and industrial parks. These projects often require imported machinery and equipment from China, contributing to the export value.
The Challenges
One of the main economic challenges in Ethiopia-China trade relations is the trade imbalance between the two countries. Ethiopia primarily exports raw materials such as agricultural products and minerals to China, while importing manufactured goods and machinery. This trade imbalance has resulted in Ethiopia being heavily dependent on China for imports, which can hinder the development of its domestic industries.
Another economic challenge is the issue of market access. Despite the growing trade volume between Ethiopia and China, Ethiopian exporters often face difficulties in accessing the Chinese market due to non-tariff barriers, such as complex regulations and standards. This can limit the export opportunities for Ethiopian businesses and hinder their competitiveness in the Chinese market.
Opportunities
There are opportunities to further enhance and boost their bilateral trade. Both countries have recognized the potential benefits of strengthening economic ties, and efforts have been made to promote trade and investment between them. In this comprehensive response, we will explore various opportunities that can contribute to boosting Ethiopia and China trade.
1.Trade Promotion Initiatives: Another opportunity to boost Ethiopia and China trade is through trade promotion initiatives. Both countries can organize trade fairs, exhibitions, and business forums to showcase their respective products and services. These events provide a platform for Ethiopian and Chinese businesses to interact, establish contacts, negotiate deals, and explore potential partnerships.
Additionally, government agencies can facilitate matchmaking between Ethiopian and Chinese companies by organizing business delegations and trade missions. Such initiatives help foster business relationships, increase market access, and promote bilateral trade.
2. Financial Cooperation: Strengthening financial cooperation between Ethiopia and China can also contribute to boosting trade. Chinese financial institutions can provide loans, credit lines, and investment capital to Ethiopian businesses for trade-related activities.
Moreover, establishing banking relationships between Ethiopian and Chinese banks can facilitate trade finance, payment settlements, and foreign exchange transactions. Financial cooperation can help overcome the challenges associated with limited access to capital and liquidity, thereby promoting trade between the two countries.
In conclusion, Ethiopia-China trade relations face various challenges, including trade imbalance, market access issues, concerns about the impact of Chinese investment on local industries, governance issues, environmental concerns, labor rights violations, and cultural barriers.
Addressing these challenges requires efforts from both countries to promote fair trade practices, improve transparency and accountability, protect the environment, ensure labor rights, and enhance cultural exchange.